Resource Pooling
Availability
This feature is available since openGauss 3.1.1.
Introduction
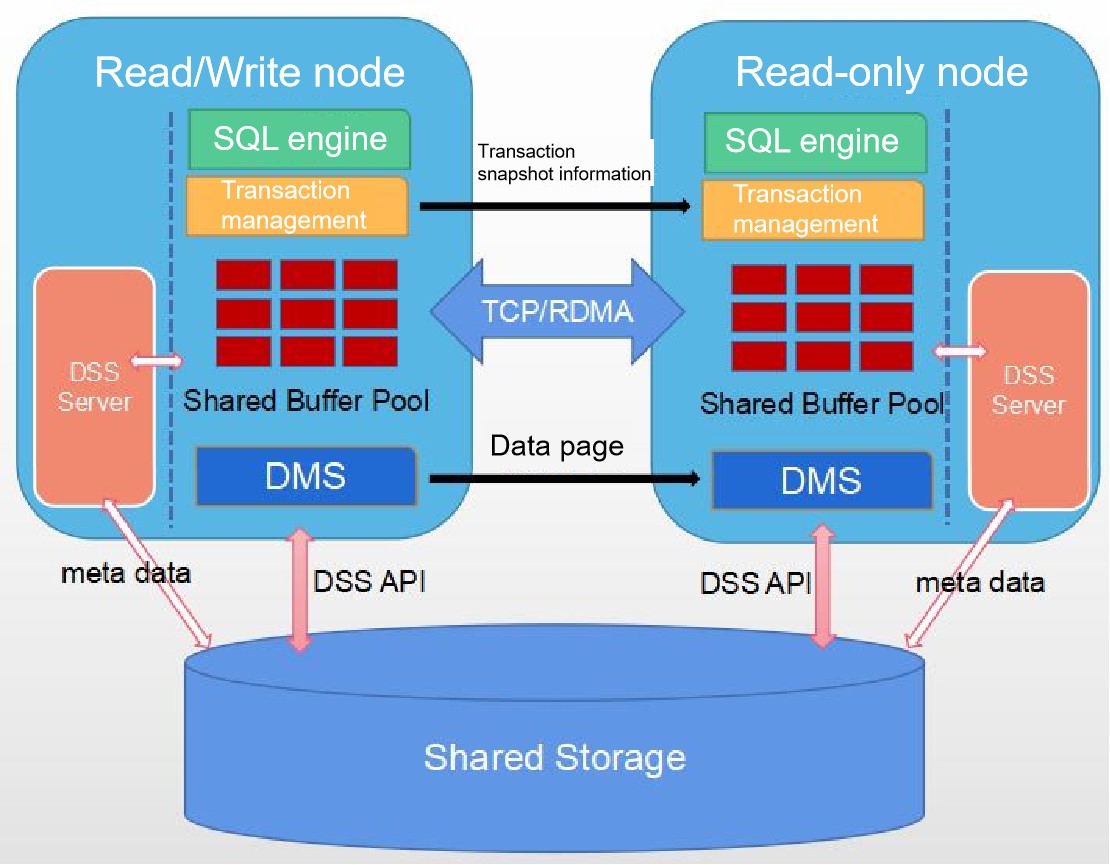
This feature enables the primary and standby nodes to share the same storage, implementing resource pooling HA deployment based on disk arrays. This solves the problem that the storage capacity is doubled compared with that of a single server in traditional HA deployment. In addition, the standby server supports real-time consistent read. The following figure shows the resource pooling architecture.
Figure 1 Resource pooling architecture
Benefits
In traditional HA deployment mode, the storage capacity is doubled compared with that of a single node, reducing the storage capacity. The standby node supports real-time consistent read, fully utilizing the computing power of multiple primary/standby nodes.
Description
The resource pooling depends on two Huawei-developed components:
Distributed storage service (DSS)
DSS is classified into DSS API and DSS server. The DSS server is an independent process that directly manages raw devices of disk arrays and provides capabilities similar to distributed file systems for external systems. The DSS API is a dynamic library integrated in the database. The DSS component uses the shared memory and client API dynamic library to provide the database with the capabilities of creating files, deleting files, expanding and shrinking files, and reading and writing files.
Distributed Memory Service (DMS)
DMS is a dynamic library integrated in the database. It transmits page content through the TCP/RDMA network, integrates the primary and standby memories, and provides the memory pooling capability to implement real-time consistent read on the standby node.
Storage pooling uses the DSS component to enable the primary and standby nodes to share the same storage. Compared with traditional database creation, resource pooling classifies directories into three types: exclusively used and not shared by each instance, exclusively used and shared by each instance, and shared by all instances. The directories to be shared must be stored on the disk array, and the directories that are not shared must be stored on the local disk. In addition, to create a database on the standby node, you only need to create a directory that belongs to the standby node. You do not need to create a directory structure shared by all instances. GUC parameters are added to the resource pooling, and the storage mode of system catalogs is switched from page mode to segment-page mode.
Memory pooling uses the DMS component to implement real-time page exchange between the primary and standby nodes and ensure real-time data consistency on standby nodes. That is, after a transaction is committed on the primary node, the transaction can be read on the standby node immediately. There is no delayed read (the transaction isolation level is read committed).
Memory pooling can use OCK RDMA to reduce the DMS primary/standby page switching latency. Compared with the latency of read consistency on a standby node in TCP mode, when OCK RDMA is enabled, the latency is reduced by at least 20%.
Enhancements
In version 5.0.0, this feature is enhanced as follows:
- Resource pooling can be upgraded from 5.0.0 to a later version.
Constraints
- The resource pooling solution depends on disk arrays. The LUN of the disk array must support the SCSI-3 PR protocol, including PERSISTENT RESERVE OUT (PR OUT), PERSISTENT RESERVE IN (PR IN), and INQUIRY, to implement cluster IO FENCE. In addition, the COMPARE AND WRITE (CAW) protocol of SCSI-3 must be supported to implement shared disk locks. For example, Dorado 5000 V3 disk array.
- The HA deployment mode implemented by resource pooling supports a maximum of one primary node and seven standby nodes.
- Resource pooling depends on functions similar to the distributed file system to implement the real-time read consistency on standby nodes. Therefore, the less the file metadata changes, the better. To ensure performance, this feature supports only segment-page tables.
- The primary and standby nodes must be deployed on the same disk array. DR deployment and hybrid deployment of the primary and standby nodes are not supported. For example, the primary and standby nodes are deployed on different disk arrays.
- Page exchange between the primary and standby nodes is accelerated by RDMA, depending on the CX5 NIC and OCK RDMA dynamic library.
- Currently, standby node rebuild, node replacement, and node restoration are not supported.
- Databases in resource pooling mode and databases in traditional mode cannot be upgraded to each other.
- In resource pooling mode, the following functions cannot be used: gs_xlogdump_xid, gs_xlogdump_lsn, gs_xlogdump_tablepath, gs_xlogdump_parsepage_tablepath, pg_create_logical_replication_slot, gs_verify_and_tryrepair_page, gs_repair_page, and gs_repair_file.
- In resource pooling mode, the following subscription functions are not supported: T_CreatePublicationStmt, T_AlterPublicationStmt, T_CreateSubscriptionStmt, T_AlterSubscriptionStmt, and T_DropSubscriptionStmt.
- Global temporary tables are not supported in resource pooling mode.
Dependencies
None.