Core Database Technologies
- [Basic Functions Oriented to Application Development](#Basic Functions Oriented to Application Development)
- High Performance
- High Scalability
- HA
- Maintainability
- Database Security
- AI Capabilities
Basic Functions Oriented to Application Development
Standard SQL
openGauss supports standard SQL statements. The SQL standard is an international standard and is updated periodically. SQL standards are classified into core features and optional features. Most databases do not fully support SQL standards. SQL features are built by database vendors to maintain customers and push up application migration costs. New SQL features are increasingly different among vendors. Currently, there is no authoritative SQL standard test.
openGauss supports most of the SQL:2011 core features and some optional features. For details about the feature list, see “SQL Reference > SQL Syntax” in the Developer Guide.
The introduction of standard SQL provides a unified SQL interface for all database vendors, reducing the learning costs of users and openGauss application migration costs.
Standard Development Interfaces
Standard ODBC and JDBC interfaces are provided to ensure quick migration of user services to openGauss.
Currently, the standard ODBC 3.5 and JDBC 4.0 interfaces are supported. The ODBC interface supports SUSE Linux, Windows 32-bit, and Windows 64-bit platforms. The JDBC interface supports all platforms.
Multiple Storage Engines
openGauss is based on the unified transaction mechanism, log system, concurrency control system, metadata information, and cache management, provides Table Access Method API, and supports different storage engines.
Currently, the Astore and Ustore storage engines are supported.
Transaction Support
Transaction support refers to the system capability to ensure the atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability (ACID) features of global transactions.
Transaction support and data consistency assurance are the basic functions of most databases and the prerequisites for a database to satisfy transaction-based application requirements.
Atomicity
A transaction is comprised of an indivisible unit of work. Operations performed in a transaction must be all finished or have not been performed.
Consistency
Transactions must be consistent within a system no matter when or how many concurrent transactions are ongoing.
Isolation
Transactions are isolated for execution, as if each of them is the only operation performed during the specified period planned by the system. If there are two transactions that are executed within the same period of time and performing the same function, the transaction isolation makes each of them regard itself as the only transaction using the system.
Durability
After a transaction is complete, the changes made by the transaction to the database are permanently stored in the database and will not be rolled back.
The default transaction isolation level is READ COMMITTED, ensuring no dirty data will be read.
Transactions are categorized into single-statement transactions and transaction blocks. Their basic interfaces are as follows:
- Start transaction;
- Commit;
- Rollback;
Set transaction (used for setting the isolation level, read/write mode, and delay mode). For details about the syntax, see the Developer Guide.
Support for Functions and Stored Procedures
Functions are important database objects. They encapsulate SQL statement sets used for certain functions so that the statements can be easily invoked.
A stored procedure is a combination of SQL and PL/SQL. Stored procedures can move the code that executes business rules from the application to the database. Therefore, the code storage can be used by multiple programs at a time.
- Allows customers to modularize program design and encapsulate SQL statement sets, easy to invoke.
- Caches the compilation results of stored procedures to accelerate SQL statement set execution.
- Allows system administrators to restrict the permission for executing a specific stored procedure and controls access to the corresponding type of data. This prevents access from unauthorized users and ensures data security.
- To process SQL statements, the stored procedure process assigns a memory fragment to store context association. Cursors are handles or pointers to context areas. With cursors, stored procedures can control alterations in context areas.
- Six levels of exception information are supported to facilitate the debugging of stored procedures. Stored procedure debugging is a debugging method. During the development of a stored procedure, you can trace the process executed by the stored procedure step by step and find the error cause or program bug based on the variable value to improve the fault locating efficiency. You can set breakpoints and perform independent debugging.
openGauss supports functions and stored procedures in the SQL standard, which enhances the usability of stored procedures. For details about how to use the stored procedures, see the Developer Guide.
PG Interface Compatibility
Compatible with PostgreSQL clients and interfaces.
SQL Hints
SQL hints are supported, which can override any execution plan and thus improve SQL query performance.
In plan hints, you can specify a join order; join, stream, and scan operations; and the number of rows in a result to tune an execution plan, improving query performance.
Copy Interface for Error Tolerance
openGauss provides the encapsulated copy error tables for creating functions and allows users to specify error tolerance options when using the Copy From statement. In this way, errors related to parsing, data format, and character set during the execution of the Copy From statement are recorded in the error table instead of being reported and interrupted. Even if a small amount of data in the target file of Copy From is incorrect, the data can be imported to the database. You can locate and rectify the fault in the error table later.
High Performance
CBO Optimizer
The openGauss optimizer is a typical Cost-based Optimization (CBO). By using CBO, the database calculates the number of tuples and the execution cost for each execution step under each execution plan based on the number of table tuples, column width, NULL record ratio, and characteristic values, such as distinct, MCV, and HB values, and certain cost calculation methods. The database then selects the execution plan that takes the lowest cost for the overall execution or for the return of the first tuple.
The CBO optimizer can select the most efficient execution plan among multiple plans based on the cost to meet customer service requirements to the maximum extent.
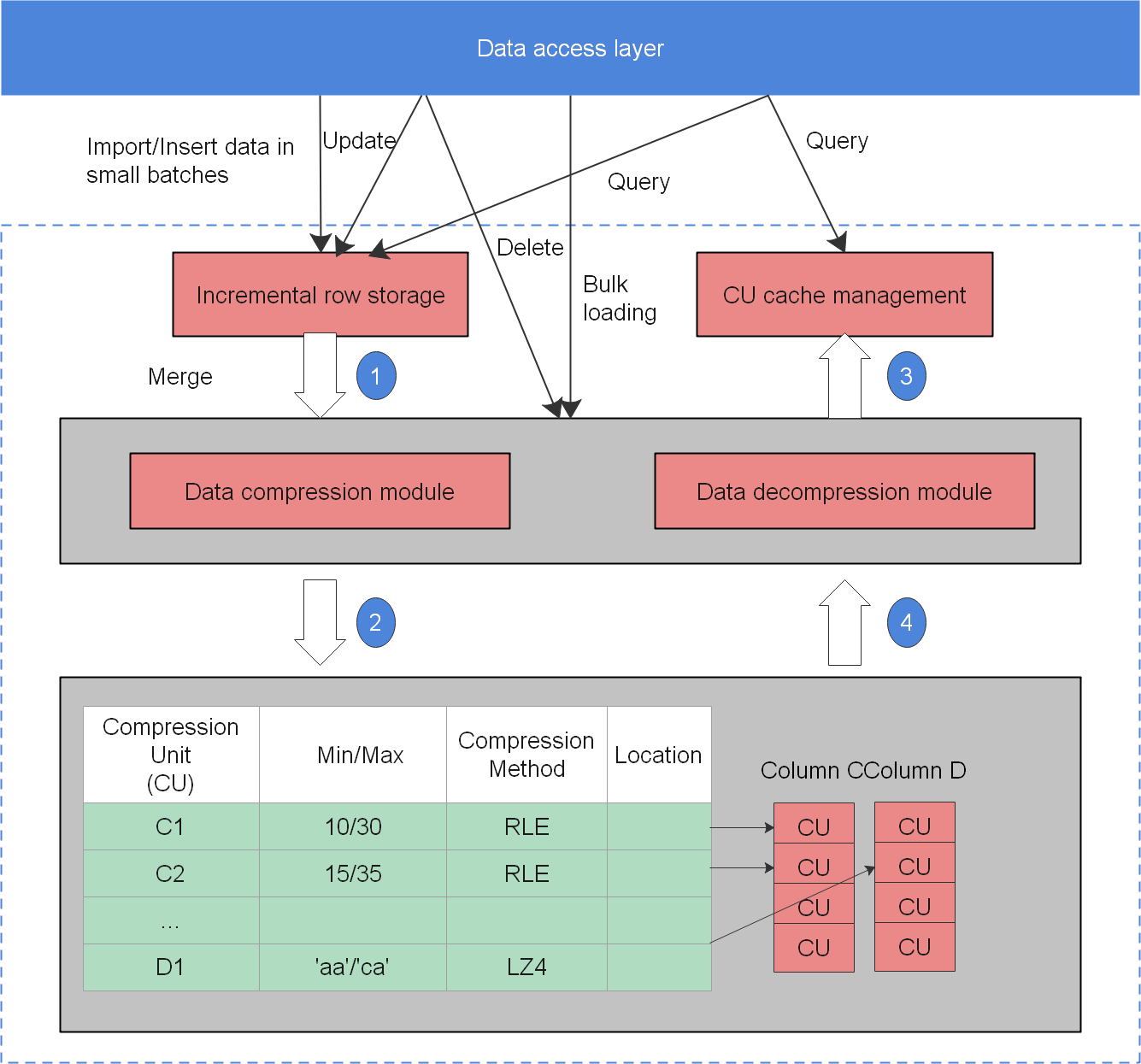
Hybrid Row-Column Storage
openGauss supports both row-store and column-store models. Users can choose a row-store or column-store table based on their needs.
Column-store is recommended if a table contains many columns (called a wide table) but its query involves only a few columns. Row-store is recommended if a table contains only a few columns and a query involves most of the columns.
Figure 1 shows the column-store model.
In a wide table containing a huge amount of data, a query usually only includes certain columns. In this case, the query performance of the row-store engine is poor. For example, a single table containing the data of a meteorological agency has 200 to 800 columns. Among these columns, only 10 are frequently accessed. In this case, a vectorized execution and column-store engine can significantly improve performance by saving storage space.
Row-store tables and column-store tables have their own advantages and disadvantages. You are advised to select a table based on the site requirements.
Row-store table
Row-store tables are created by default. Data is stored by row. Row-store supports adding, deleting, modifying, and querying data of a complete row. Therefore, this storage model applies to scenarios where data needs to be updated frequently.
Column-store table
Data is stored by column. The I/O of data query in a single column is small, and column-store tables occupy less storage space than row-store tables. This storage model applies to scenarios where data is inserted in batches, less updated, and queried for statistical analysis. The performance of single point query and single record insertion in a column-store table is poor.
The principles for selecting row-store and column-store tables are as follows:
Update frequency
If data is frequently updated, use a row-store table.
Insert frequency
If a small amount of data is frequently inserted each time, use a row-store table. If a large amount of data is inserted at a time, use column storage.
Number of columns
If a table is to contain many columns, use a column-store table.
Number of columns to be queried
If only a small number of columns (less than 50% of the total) is queried each time, use a column-store table.
Compression ratio
The compression ratio of a column-store table is higher than that of a row-store table. The higher the compression ratio is, the more CPU resources will be consumed.
In-place Upate Storage
The in-place update storage engine solves the problems of space expansion and large tuples of the Append update storage engine. The design of efficient rollback segments is the basis of the in-place update storage engine.
Xlog Lockless Update and Parallel Page Playback
Figure 2 Xlog lock less Design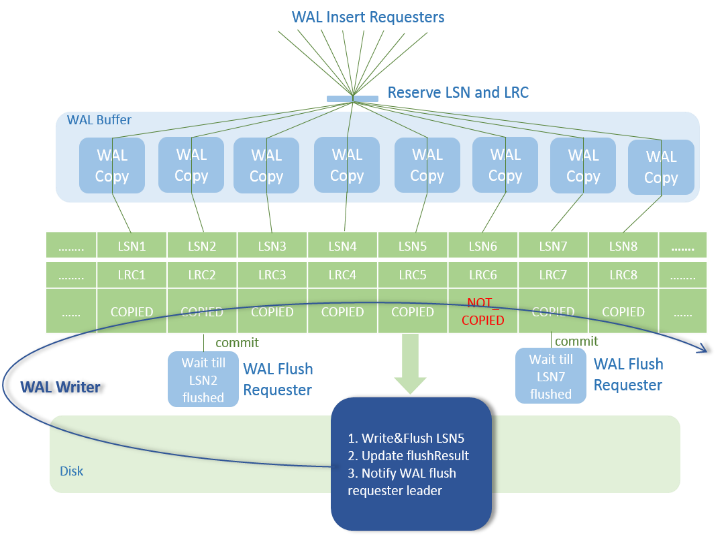
This feature optimizes the WalInsertLock mechanism by using log sequence numbers (LSNs) and log record counts (LRCs) to record the copy progress of each backend and canceling the WalInsertLock mechanism. The backend can directly copy logs to the WalBuffer without contending for the WalInsertLock. In addition, a dedicated WALWriter thread is used to write logs, and the backend thread does not need to ensure the Xlog flushing. After the preceding optimization, the WalInsertLock contention and WalWriter dedicated disk write threads are canceled. The system performance can be further improved while the original XLog function remains unchanged. This feature optimizes the Ustore in-place update WALs and Ustore DML operation parallel playback and distribution. Prefixes and suffixes are used to reduce the update WALs. The playback thread is divided into multiple types to solve the problem that most Ustore DML WALs are replayed on multiple pages. In addition, the Ustore data page playback is distributed based on blkno to improve the degree of parallel playback.
Adaptive Compression
Currently, mainstream databases usually use the data compression technology. Various compression algorithms are used for different data types. If pieces of data of the same type have different characteristics, their compression algorithms and results will also be different. Adaptive compression chooses the suitable compression algorithm for data based on the data type and characteristics, achieving high performance in compression ratio, import, and query.
Importing and frequently querying a huge amount of data are the main application scenarios. When you import data, adaptive compression greatly reduces the data volume, increases I/O operation efficiency several times, and clusters data before storage, achieving fast data import. In this way, only a small number of I/O operations is required and data is quickly decompressed in a query. Data can be quickly retrieved and the query result is quickly returned.
Currently, the database has implemented various compression algorithms, including RLE, DELTA, BYTEPACK/BITPACK, LZ4, ZLIB, and LOCAL DICTIONARY. The following table lists data types and the compression algorithms suitable for them.
For example, large integer compression of mobile number-like character strings, large integer compression of the numeric type, and adjustment of the compression algorithm compression level are supported.
Partition
In the openGauss system, data is partitioned horizontally on an instance using a specified policy. This operation splits a table into multiple partitions that are not overlapped.
In common scenarios, a partitioned table has the following advantages over a common table:
- High query performance: You can specify partitions when querying partitioned tables, improving query efficiency.
- High availability: If a certain partition in a partitioned table is faulty, data in the other partitions is still available.
- Easy maintenance: If a partition in a partitioned table is faulty, only this partition needs to be repaired.
- Balanced I/O: Partitions can be mapped to different disks to balance I/O and improve the overall system performance.
Currently, openGauss supports range partitioned tables, list partitioned tables, and hash partitioned tables.
In a range partitioned table, data within a certain range is mapped to each partition. The range is determined by the partition key specified when the partitioned table is created. This partitioning mode is most commonly used.
With the range partitioning function, the database divides a record, which is to be inserted into a table, into multiple ranges using one or multiple columns and creates a partition for each range to store data. Partition ranges do no overlap.
In a list partitioned table, data is mapped to each partition based on the key values contained in each partition. The key values contained in a partition are specified when the partition is created.
The list partitioning function divides the key values in the records to be inserted into a table into multiple lists (the lists do not overlap in different partitions) based on a column of the table, and then creates a partition for each list to store the corresponding data.
In a hash partitioned table, data is mapped to each partition using the hash algorithm, and each partition stores records with the same hash value.
The hash partitioning function uses the internal hash algorithm to divide records to be inserted into a table into partitions based on a column of the table.
If you specify the PARTITION parameter when running the CREATE TABLE statement, data in the table will be partitioned.
Users can modify partition keys as needed during table creation to make the query result stored in the same or least partitions (called partition pruning), so as to obtain consecutive I/O to improve the query performance.
In actual services, time is often used as a filter criterion for query objects. Therefore, you can select the time column as the partition key. The key value range can be adjusted based on the total data volume and the data volume queried at a time.
SQL Bypass
In a typical OLTP scenario, simple queries account for a large proportion. This type of queries involves only single tables and simple expressions. To accelerate such query, the SQL bypass framework is proposed. After simple mode judgment is performed on such query at the parse layer, the query enters a special execution path and skips the classic execution framework, including operator initialization and execution, expression, and projection. Instead, it directly rewrites a set of simple execution paths and directly invokes storage interfaces, greatly accelerating the execution of simple queries.
Kunpeng NUMA Architecture Optimization
Figure 2 Kunpeng NUMA architecture optimization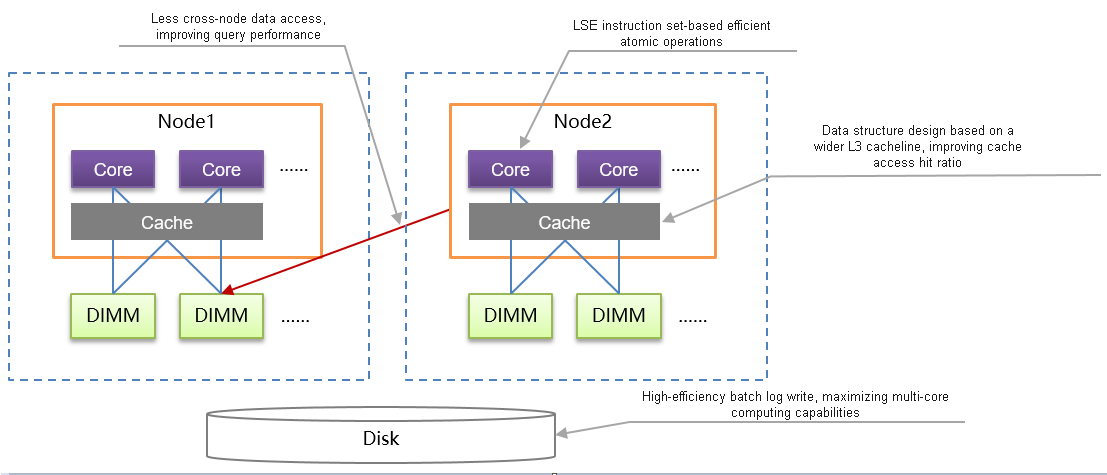
- Based on the multi-core NUMA architecture of the Kunpeng processor, openGauss optimizes the NUMA architecture to reduce the cross-core memory access latency and maximize the multi-core Kunpeng computing capability. The key technologies include redo log batch insertion, NUMA distribution of hotspot data, and Clog partitions, greatly improving the processing performance of the TP system.
- Based on the ARMv8.1 architecture used by the Kunpeng chip, openGauss uses the LSE instruction set to implement efficient atomic operations, effectively improving the CPU usage, multi-thread synchronization performance, and XLog write performance.
- Based on the wider L3 cacheline provided by the Kunpeng chip, openGauss optimizes hotspot data access, effectively improving the cache access hit ratio, reducing the cache consistency maintenance overhead, and greatly improving the overall data access performance of the system.
High Concurrency of the Thread Pool
In the OLTP field, a database needs to process a large quantity of client connections. Therefore, the processing capability in high-concurrency scenarios is one of the important capabilities of the database.
The simplest processing mode for external connections is the per-thread-per-connection mode, in which a user connection generates a thread. This mode features simple processing thanks to its architecture. However, in high-concurrency scenarios, there are too many threads, causing heavy workload in thread switchover and large conflict between the lightweight lock areas of the database. As a result, the performance (throughput) deteriorates sharply and the SLA of user performance cannot be met.
Therefore, a thread resource pooling and reuse technology needs to be used to resolve this problem. The overall design idea of the thread pool technology is to pool thread resources and reuse them among different connections. After the system is started, a fixed number of working threads are started based on the current number of cores or user configuration. A working thread serves one or more connection sessions. In this way, the session and thread are decoupled. The number of worker threads is fixed. Therefore, frequent thread switchover does not occur in case of high concurrency. The database layer schedules and manages sessions.
Parallel Query
The Symmetric Multi-Processing (SMP) parallel technology of openGauss uses the multi-core CPU architecture of a computer to implement multi-thread parallel computing, fully using CPU resources to improve query performance. In complex query scenarios, a single query execution takes long time and the system concurrency is low. Therefore, the SMP parallel execution technology is used to implement operator-level parallel execution, which effectively reduces the query execution time and improves the query performance and resource utilization. The overall implementation of the SMP parallel technology is as follows: For query operators that can be executed in parallel, data is sliced, multiple working threads are started for computation, and then the results are summarized and returned to the frontend. The data interaction operator Stream is added to SMP parallel execution to implement data interaction between multiple working threads, ensuring the correctness of the query and completing the overall query.
Dynamic Build and Execution
Based on the query execution plan tree, with the library functions provided by the LLVM, openGauss moves the process of determining the actual execution path from the executor phase to the execution initialization phase. In this way, problems such as function calling, logic condition branch determination, and a large amount of data reading that are related to the original query execution are avoided, to improve the query performance.
High Scalability
High Concurrency of the Thread Pool
In the OLTP field, a database needs to process a large quantity of client connections. Therefore, the processing capability in high-concurrency scenarios is one of the important capabilities of the database.
The simplest processing mode for external connections is the per-thread-per-connection mode, in which a user connection generates a thread. This mode features simple processing thanks to its architecture. However, in high-concurrency scenarios, there are too many threads, causing heavy workload in thread switchover and large conflict between the lightweight lock areas of the database. As a result, the performance (throughput) deteriorates sharply and the SLA of user performance cannot be met.
Therefore, a thread resource pooling and reuse technology needs to be used to resolve this problem. The overall design idea of the thread pool technology is to pool thread resources and reuse them among different connections. After the system is started, a fixed number of working threads are started based on the current number of cores or user configuration. A working thread serves one or more connection sessions. In this way, the session and thread are decoupled. The number of worker threads is fixed. Therefore, frequent thread switchover does not occur in case of high concurrency. The database layer schedules and manages sessions.
HA
Primary/Standby
To ensure that a fault can be rectified, data needs to be written into multiple copies. Multiple copies are configured for the primary and standby nodes, and logs are used for data synchronization. In this way, openGauss has no data lost when a node is faulty or the system restarts after a stop, meeting the ACID feature requirements. The primary/standby environment supports two modes: primary/standby, and one primary and multiple standbys. In primary/standby mode, if the standby node needs to redo logs, it can be promoted to primary. In the one primary and multiple standbys mode, all standby nodes need to redo logs and can be promoted to primary. The primary/standby mode is mainly used for OLTP systems with general reliability to save storage resources. The one primary and multiple standbys mode provides higher DR capabilities and is suitable for the OLTP system with higher availability transaction processing.
The switchover command can be used to trigger a switchover between the primary and standby nodes. If the primary node is faulty, the failover command can be used to promote the standby node to the primary.
To ensure that the failover time is controllable, you can enable the log flow control function to control the rate of sending logs to the standby node. This ensures that the logs accumulated on the standby node will be replayed within the time configured for flow control. After flow control is enabled, the rate of sending logs to the standby node is dynamically adjusted. As a result, the overall transaction performance deteriorates.
In scenarios such as initial installation or backup and restoration, data on the standby node needs to be rebuilt based on the primary node. In this case, the build function is required to send the data and WALs of the primary node to the standby node. When the primary node is faulty and joins again as a standby node, the build function needs to be used to synchronize data and WALs with those of the new primary node. Build includes full build and incremental build. Full build depends on primary node data for rebuild. The amount of data to be copied is large and the time required is long. Incremental build copies only differential files. The amount of data to be copied is small and the time required is short. Generally, the incremental build is preferred for fault recovery. If the incremental build fails, the full build continues until the fault is rectified.
In addition to streaming replication in primary/standby mode, openGauss also supports logical replication. In logical replication, the primary database is called the source database, and the standby database is called the target database. The source database parses the WAL file based on the specified logical parsing rule and parses the DML operation into certain logical change information (standard SQL statements). The source database sends standard SQL statements to the target database. After receiving the SQL statements, the target database applies them to implement data synchronization. Logical replication involves only DML operations. Logical replication can implement cross-version replication, heterogeneous database replication, dual-write database replication, and table-level replication.
Logical Backup
openGauss provides the logical backup capability to back up data in user tables to local disk files in text or CSV format and restore the data in homogeneous or heterogeneous databases.
Physical Backup
openGauss provides the physical backup capability to back up data of the entire instance to local disk files in the internal database format, and restore data of the entire instance in a homogeneous database.
Physical backup is classified into full backup and incremental backup. The difference is as follows: Full backup includes the full data of the database at the backup time point. The time required for full backup is long (in direct proportion to the total data volume of the database), and a complete database can be restored. Incremental backup involves only incremental data modified after a specified time point. It takes a short period of time (in direct proportion to the incremental data volume and irrelevant to the total data volume). However, a complete database can be restored only after the incremental backup and full backup are performed. openGauss supports both full and incremental backup modes.
Flashback Restoration
The flashback function is used to restore dropped tables from the recycle bin. Like in a Window OS, dropped table information is stored in the recycle bin of databases. The MVCC mechanism is used to restore data to a specified point in time or system change number (SCN).
Ultimate RTO
After the ultimate RTO function is enabled, multi-level pipelines are established for Xlog log playback to improve the concurrency and log playback speed.
When the service load is heavy, the playback speed of the standby node cannot catch up with that of the primary node. After the system runs for a long time, logs are accumulated on the standby node. If a host is faulty, data restoration takes a long time and the database is unavailable, which severely affects system availability. The ultimate recovery time object (RTO) is enabled to reduce the data recovery time after a host fault occurs and improve availability.
Logical Replication
openGauss provides the logical decoding function to reversely parse physical logs into logical logs. Logical replication tools such as DRS convert logical logs to SQL statements and replay the SQL statements in the peer database. In this way, data can be synchronized between heterogeneous databases. Currently, unidirectional and bidirectional logical replication between the openGauss database and the MySQL or Oracle database is supported. DNs reversely parse physical logs to logical logs. Logical replication tools such as DRS extract logical logs from DNs, convert the logs to SQL statements, and replay the SQL statements in MySQL. Logical replication tools also extract logical logs from a MySQL database, reversely parse the logs to SQL statements, and replay the SQL statements in openGauss. In this way, data can be synchronized between heterogeneous databases.
Point-In-Time Recovery (PITR)
PITR uses basic hot backup, WALs, and WAL archive logs for backup and recovery. When replaying a WAL record, you can stop at any point in time, so that there is a snapshot of the consistent database at any point in time. That is, you can restore the database to the state at any time since the backup starts. During recovery, openGauss supports specifying the recovery stop point as TID, time, and LSN.
High Availability Based on the Paxos Protocol (DCF)
After DCF is enabled, DNs support Paxos-based replication and quorum, achieving high availability and disaster recovery. DNs support automatic primary node selection and log replication. The replication process supports compression and stream control to prevent high bandwidth usage. Node types based on Paxos roles are provided and can be adjusted.
Two-City Three-DC DR
Two-city three-DC indicates that the three DCs (production center, intra-city DR center, and remote DR center) are deployed in two cities. In recent years, natural disasters have occurred frequently at home and abroad. The two-city three-DC DR solution comes into being with the combination of two intra-city DCs and remote DR DCs. This solution features high availability and disaster backup capabilities. The two intra-city DCs are two data centers that can carry critical applications independently. They have similar data processing capabilities and can synchronize data in real time through high-speed links. Under normal circumstances, the two DCs manage services and system operation together and can be switched over. When disaster occurs, services can be switched over to the DR DC with almost no data loss, ensuring service continuity. Compared with the remote DR DC, two intra-city DCs have lower investment cost, faster building speed, easier operation and maintenance, and higher reliability. A remote DR DC is deployed in a different city and is used to back up data of the two DCs. When faults occur in the two DCs, the remote DR DC can recover services from backup data.
Specifications
Streaming replication-based remote DR solution:
The network latency within the primary or DR database instance must be less than or equal to 10 ms, and the network latency between the primary and standby database instances must be less than or equal to 100 ms. The DR can run normally within the range of the required network latency. Otherwise, the primary and standby nodes will be disconnected.
The following table lists the log generation speeds in the primary database instance supported by different hardware specifications when the network bandwidth is not a bottleneck and the parallel playback function is enabled in the DR database instance. The RPO and RTO can be ensured only under the log generation speed.
Table 1 Log generation speed supported by different hardware specifications
A certain amount of data can be lost when the DR database instance is promoted to primary, and the RPO is less than or equal to 10 seconds. When the DR database instance is normal, the RTO for promoting the DR database instance to primary is less than or equal to 10 minutes. When the DR database instance is degraded, the RTO for promoting the DR database instance to primary is within 20 minutes.
Practice: Planned primary/standby database instance switchover, no data loss, RPO = 0, RTO ≤ 20 minutes (including the processes of demoting the primary database instance to the DR instance and promoting the DR database instance to the primary database instance)
 NOTICE:
Tests show that the maximum write rate of SATA SSDs is about 240 MB/s, that of SAS SSDs is over 500 MB/s, and that of NVMe SSDs is even better. Currently, only the performance metric under the SATA SSD hardware specifications is provided. If the hardware conditions do not meet the preceding specifications, the single-shard log generation speed in the primary database instance must be reduced to ensure the RPO and RTO.
NOTICE:
Tests show that the maximum write rate of SATA SSDs is about 240 MB/s, that of SAS SSDs is over 500 MB/s, and that of NVMe SSDs is even better. Currently, only the performance metric under the SATA SSD hardware specifications is provided. If the hardware conditions do not meet the preceding specifications, the single-shard log generation speed in the primary database instance must be reduced to ensure the RPO and RTO.Resources such as file handles and memory are used up in the primary and standby database instances. As a result, the RPO and RTO cannot be ensured.
Maintainability
Workload Diagnosis Report
The workload diagnosis report (WDR) generates a performance report between two different time points based on the system performance snapshot data at two different time points. The report is used to diagnose database kernel performance faults.
WDR depends on the following two components:
- SNAPSHOT: The performance snapshot can be configured to collect a certain amount of performance data from the kernel at a specified interval and store the data in the user tablespace. Any snapshot can be used as a performance baseline for comparison with other snapshots.
- WDR Reporter: This tool analyzes the overall system performance based on two snapshots, calculates the changes of more specific performance indicators between the two time periods, and generates summarized and detailed performance data. For details, see Table 1 and Table 2.
Table 1 Summarized diagnosis report
Table 2 Detailed diagnosis report
Benefits:
- WDR is the main method for diagnosing long-term performance problems. Based on the performance baseline of a snapshot, performance analysis is performed from multiple dimensions, helping DBAs understand the system load, performance of each component, and performance bottlenecks.
- Snapshots are also an important data source for subsequent performance problem self-diagnosis and self-optimization suggestions.
Slow SQL Diagnosis
Slow SQL records information about all jobs whose execution time exceeds the threshold.
Historical slow SQL provides table-based and function-based query interfaces. You can query the execution plan, start time, end time, query statement, row activity, kernel time, CPU time, execution time, parsing time, compilation time, query rewriting time, plan generation time, network time, I/O time, network overhead, lock overhead, and wait event. All information is anonymized.
Slow SQL provides detailed information required for slow SQL diagnosis. You can diagnose performance problems of specific slow SQL statements offline without reproducing the problem. The table-based and function-based APIs help users collect statistics on slow SQL indicators and connect to third-party platforms.
Both primary and standby nodes support slow SQL diagnosis.
Database Security
Access Control
Access control is to manage users' database access control permissions, including database system permissions and object permissions.
Role-based access control is supported. Roles and permissions are associated. Permissions are assigned to roles and then roles are assigned to users, implementing user access control permission management. The login access control is implemented by using the user ID and authentication technology. The object access control is implemented by checking the object permission based on the user permission on the object. You can assign the minimum permissions required for completing tasks to related database users to minimize database usage risks.
An access control model based on separation of permissions is supported. Database roles are classified into system administrator, security administrator, and audit administrator. The security administrator creates and manages users, the system administrator grants and revokes user permissions, and the audit administrator audits all user behaviors.
By default, the role-based access control model is used. You can set parameters to determine whether to enable the access control model based on separation of permissions.
Separation of Control and Access Permissions
For the system administrator, the control and access permissions on table objects are separated to improve data security of common users and restrict the object access permissions of administrators.
This feature applies to the following scenarios: An enterprise has multiple business departments using different database users to perform service operations. Database maintenance departments at the same level use the database administrator to perform O&M operations. The business departments require that administrators can only perform control operations (DROP, ALTER, and TRUNCATE) on data of each department and cannot perform access operations (INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE, SELECT, and COPY) without authorization. That is, the control permissions of database administrators for tables need to be isolated from their access permissions to improve the data security of common users.
The system administrators can specify the INDEPENDENT attribute when creating a user, indicating that the user is a private user. Database administrators (including initial users and other administrators) can control (DROP, ALTER, and TRUNCATE) objects of private users but cannot access (INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE, SELECT, COPY, GRANT, REVOKE, and ALTER OWNER) the objects without authorization.
Built-in Database Role Permission Management
openGauss provides a group of default roles whose names start with gs_role_. These roles are provided to access to specific, typically high-privileged operations. You can grant these roles to other users or roles within the database so that they can use specific functions. These roles should be given with great care to ensure that they are used where they are needed. Table 1 describes the permissions of built-in roles.
Table 1 Built-in role permissions
Database Encryption Authentication
The password encryption method based on the RFC5802 mechanism is used for authentication.
The unidirectional, irreversible Hash encryption algorithm PBKDF2 is used for encryption and authentication, effectively defending against rainbow attacks.
The password of the created user is encrypted and stored in the system catalog. During the entire authentication process, passwords are encrypted for storage and transmission. The hash value is calculated and compared with the value stored on the server to verify the correctness.
The message processing flow in the unified encryption and authentication process effectively prevents attackers from cracking the username or password by capturing packets.
Database Audit
Audit logs record user operations performed on database startup and stopping, connection, and DDL, DML, and DCL operations. The audit log mechanism enhances the database capability of tracing illegal operations and collecting evidence.
You can set parameters to specify the statements or operations for which audit logs are recorded.
Audit logs record the event time, type, execution result, username, database, connection information, database object, database instance name, port number, and details. You can query audit logs by start time and end time and filter audit logs by recorded field.
Database security administrators can use the audit logs to reproduce a series of events that cause faults in the database and identify unauthorized users, unauthorized operations, and the time when these operations are performed.
Network Communication Security
SSL can be used to encrypt communication data between the client and server, ensuring communication security between the client and server.
The TLS 1.2 protocol and a highly secure encryption algorithm suite are adopted. Table 2 lists the supported encryption algorithm suites.
Table 2 Encryption algorithm suites
Row-Level Security
The row-level security (RLS) feature enables database access control to be accurate to each row of data tables. When different users perform the same SQL query operation, the read results may be different according to the RLS policy.
You can create an RLS policy for a data table. The policy defines an expression that takes effect only for specific database users and SQL operations. When a database user accesses the data table, if a SQL statement meets the specified RLS policy of the data table, the expressions that meet the specified condition will be combined by using AND or OR based on the attribute type (PERMISSIVE | RESTRICTIVE) and applied to the execution plan in the query optimization phase.
RLS is used to control the visibility of row-level data in tables. By predefining filters for data tables, the expressions that meet the specified condition can be applied to execution plans in the query optimization phase, which will affect the final execution result. Currently, RLS supports the following SQL statements: SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
Resource Labels
The resource label feature classifies database resources based on user-defined rules to implement resource classification and management. Administrators can configure resource labels to configure security policies, such as auditing or data masking, for a group of database resources.
Resource labels can be used to group database resources based on features and application scenarios. You can manage all database resources with specified labels, which greatly reduces policy configuration complexity and information redundancy and improves management efficiency.
Currently, resource labels support the following database resource types: schema, table, column, view, and function.
Dynamic Data Masking
To prevent unauthorized users from sniffing privacy data, the dynamic data masking feature can be used to protect user privacy data. When an unauthorized user accesses the data for which a dynamic data masking policy is configured, the database returns the anonymized data to protect privacy data.
Administrators can create dynamic data masking policies on data columns. The policies specify the data masking methods for specific user scenarios. After the dynamic data masking function is enabled, the system matches user identity information (such as the access IP address, client tool, and username) with the masking policy when a user accesses data in the sensitive column. After the matching is successful, the system masks the sensitive data in the query result of the column based on the masking policy.
The purpose of dynamic data masking is to flexibly protect privacy data by configuring the filter, and specifying sensitive column labels and corresponding masking functions in the masking policy without changing the source data.
Unified Auditing
Unified auditing allows administrators to configure audit policies for database resources or resource labels to simplify management, generate audit logs, reduce redundant audit logs, and improve management efficiency.
Administrators can customize audit policies for configuring operation behaviors or database resources. The policies are used to audit specific user scenarios, user behaviors, or database resources. After the unified auditing function is enabled, when a user accesses the database, the system matches the corresponding unified audit policy based on the user identity information, such as the access IP address, client tool, and username. Then, the system classifies the user behaviors based on the access resource label and user operation type (DML or DDL) in the policy to perform unified auditing.
The purpose of unified auditing is to change the existing traditional audit behavior into specific tracking audit behavior and exclude other behaviors from the audit, thereby simplifying management and improving the security of audit data generated by the database.
Password Strength Verification
To harden the security of customer accounts and data, do not set weak passwords. You need to specify a password when initializing the database, creating a user, or modifying a user. The password must meet the strength requirements. Otherwise, the system prompts you to enter the password again.
The account password complexity policy restricts the minimum number of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special characters in a password, the maximum and minimum length of a password, the password cannot be the same as the username or the reverse of the username, and the password cannot be a weak password. This policy enhances user account security.
Weak passwords are easy to crack. The definition of weak passwords may vary with users or user groups. Users can define their own weak passwords.
The password_policy parameter specifies whether to enable the password strength verification mechanism. The default value is 1, indicating that the password strength verification mechanism is enabled.
Data Encryption and Storage
Imported data is encrypted before stored.
This feature provides data encryption and decryption APIs for users and uses encryption functions to encrypt sensitive information columns identified by users, so that data can be stored in tables after being encrypted.
If you need to encrypt the entire table, you need to write an encryption function for each column. Different attribute columns can use different input parameters.
If a user with the required permission wants to view specific data, the user can decrypt required columns using the decryption function API.
Ledger Database
To prevent database O&M personnel from stealing, tampering with, and erasing traces of the database, you can use the ledger database feature to perform comprehensive audit and trace the history. When a tamper-proof user table is modified, the database records the modification behavior to the history table where only data can be appended. In this way, the operation history can be recorded and the operation source can be traced.
The ledger database stores and verifies historical operations by generating data hash digests. Ledgers refer to user history tables and global blockchain tables. For table-level data modification operations, the system records the operation information and hash digest in a global blockchain table. In addition, each tamper-proof user table corresponds to a user history table to record the hash digest of row-level data changes. You can determine whether the user table is tampered by recalculating the hash digest and verifying the hash digest consistency.
Each record in the ledger represents a given operation fact that has occurred. The content of the record can only be appended and cannot be modified. The consistency between the tamper-proof user table and the corresponding history table can be checked to identify and track the tampering behavior. In addition, the ledger database provides an API for checking the tamper-proof user table consistency and an API for restoring and archiving history tables to meet the requirements of tampering identification, data expansion and mitigation, and historical data restoration and archiving.
AI Capabilities
AI4DB
AI4DB includes intelligent parameter tuning and diagnosis, slow SQL discovery, index recommendation, time sequence prediction, and exception detection. It provides users with more convenient O&M operations and performance improvement, and implements functions such as self-tuning, self-monitoring, and self-diagnosis.
DB4AI
DB4AI is compatible with the MADlib ecosystem, supports more than 70 algorithms, and delivers performance several times higher than that of MADlib on PostgreSQL. Advanced and common algorithm suites such as XGBoost, prophet, and GBDT are added to supplement the shortcomings of the MADlib ecosystem. The technology stack from SQL to machine learning is unified to implement one-click driving of SQL statements from data management to model training.
The fenced UDF and native DB4AI algorithm capabilities are provided, including the execution plan, operators, and SQL syntax in the database.
ABO Optimizer
The ABO optimizer features that openGauss uses lightweight machine learning to optimize query plans. The current version provides two functions: intelligent cardinality estimation and adaptive plan selection.
- Intelligent cardinality estimation uses the Bayesian network algorithm in the database to improve the cardinality estimation accuracy of multi-column equality query on data with strong correlation between columns by several times, and significantly improves the end-to-end execution efficiency.
- Adaptive plan selection uses linear expansion of query selection rate to explore cache plans, and uses query selection rate range to match and select cache plans. This compensates for the defect that the execution plan cannot adapt to a single general cache plan, and avoids the cost caused by frequent calling of query optimization. In typical scenarios, the performance can be improved by several times.