Loop Statements
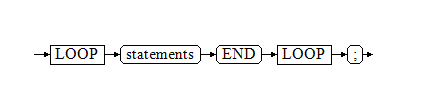
Simple LOOP Statements
Syntax diagram
Example
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_loop(i in integer, count out integer)
AS
BEGIN
count:=0;
LOOP
IF count > i THEN
raise info 'count is %. ', count;
EXIT;
ELSE
count:=count+1;
END IF;
END LOOP;
END;
/
CALL proc_loop(10,5);
NOTICE: The loop must be exploited together with EXIT; otherwise, a dead loop occurs.
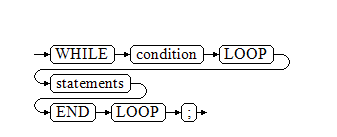
WHILE_LOOP Statements
Syntax diagram
If the conditional expression is true, a series of statements in the WHILE statement are repeatedly executed and the condition is decided each time the loop body is executed.
Example
CREATE TABLE integertable(c1 integer) ;
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_while_loop(maxval in integer)
AS
DECLARE
i int :=1;
BEGIN
WHILE i < maxval LOOP
INSERT INTO integertable VALUES(i);
i:=i+1;
END LOOP;
END;
/
-- Invoke a function.
CALL proc_while_loop(10);
-- Delete the stored procedure and table.
DROP PROCEDURE proc_while_loop;
DROP TABLE integertable;
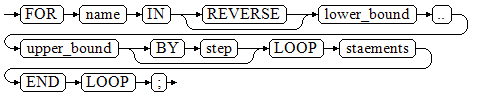
FOR_LOOP (Integer variable) Statement
Syntax diagram
NOTE:
- The variable name is automatically defined as the integer type and exists only in this loop. The value of name ranges from lower_bound to upper_bound.
- When the keyword REVERSE is used, the value of lower_bound must be greater than or equal to that of upper_bound; otherwise, the loop body is not executed.
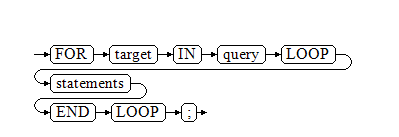
FOR_LOOP Query Statements
Syntax diagram
NOTE: The variable target is automatically defined, its type is the same as that in the query result, and it is valid only in this loop. The value of target is the query result.
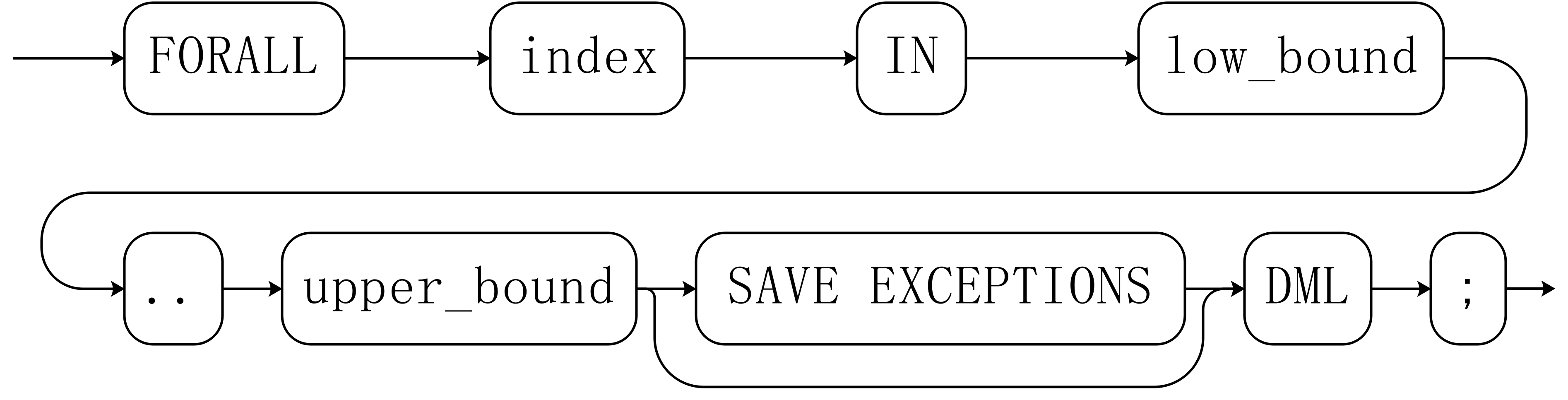
FORALL Batch Query Statements
Syntax diagram
NOTE:
- The variable index is automatically defined as the integer type and exists only in this loop. The value of index falls between the value of low_bound and the value of upper_bound.
- If SAVE EXCEPTIONS is specified, exceptions occurred during DML execution in the loop body are saved in SQL&BULK_EXCEPTIONS and an exception is thrown after the execution is complete. If there is no abnormal execution result in the loop, the loop will not be rolled back in the current subtransaction.
Example
CREATE TABLE hdfs_t1 (
title NUMBER(6),
did VARCHAR2(20),
data_period VARCHAR2(25),
kind VARCHAR2(25),
interval VARCHAR2(20),
time DATE,
isModified VARCHAR2(10)
);
INSERT INTO hdfs_t1 VALUES( 8, 'Donald', 'OConnell', 'DOCONNEL', '650.507.9833', to_date('21-06-1999', 'dd-mm-yyyy'), 'SH_CLERK' );
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_forall()
AS
BEGIN
FORALL i IN 100..120
update hdfs_t1 set title = title + 100*i;
END;
/
-- Invoke a function.
CALL proc_forall();
-- Query the invocation result of the stored procedure.
SELECT * FROM hdfs_t1 WHERE title BETWEEN 100 AND 120;
-- Delete the stored procedure and table.
DROP PROCEDURE proc_forall;
DROP TABLE hdfs_t1;
LABEL_LOOP Statements
Syntax
[label_begin:] LOOP
statements
END LOOP [label_end]
NOTE:
The usage of the label is added based on the simple loop statement. The label rules are as follows:
- label_begin can appear independently (without label_end). However, if label_end is used, label_begin must appear.
- The label can be referenced by the CONTINUE or EXIT statement. In the B-compatible database, the ITERATE or LEAVE statement can also be used.
NOTICE: This loop is used only in the B-compatible database. An error is reported in other databases. This loop must be used together with EXIT. (In B-compatible mode, LEAVE has the same effect as EXIT, and ITERATE has the same effect as CONTINUE.) Otherwise, an infinite loop occurs.
Example
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE label_loop(i in integer, count out integer)
AS
BEGIN
count:=0;
label:
LOOP
IF count > i THEN
raise info 'count is %. ', count;
LEAVE;
ELSE
count:=count+1;
END IF;
END LOOP label;
END;
/
CALL proc_loop(10,5);