Primary/Standby Shared Storage
Introduction
Shared storage enables the primary and standby nodes to share the same storage. In traditional HA deployment mode, the storage capacity is doubled compared with that of a single node. This feature provides a new HA deployment mode for the primary/standby shared storage, meeting the requirements for reducing the storage capacity and costs. In addition, OCK RDMA can be used to improve the real-time read consistency on standby nodes.
Architecture
The following figure shows the overall architecture of the primary/standby shared storage.
Figure 1 Primary/Standby shared storage architecture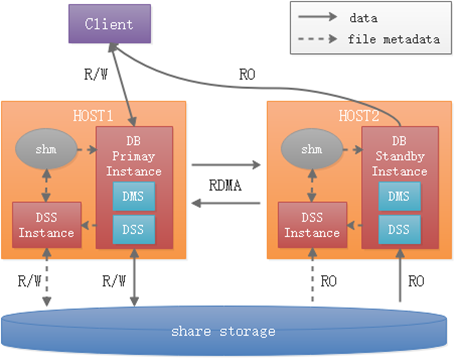
UltraPath has been installed on the disk array, and the disk array is available.
Distributed Storage Service (DSS)
The DSS process is an independent process that directly manages raw devices of disk arrays and provides capabilities similar to distributed file systems for external systems. The shared memory and client API dynamic library provide the database with the capabilities of creating files, deleting files, expanding and shrinking files, and reading and writing files.
Distributed Memory Service (DMS)
DMS is a dynamic library integrated in the database. It transmits page content through the TCP/RDMA network, integrates the primary and standby memories, and provides the memory pooling capability to implement real-time read consistency on standby nodes.
Page exchange between the primary and standby nodes is accelerated by RDMA, depending on the CX5 NIC and OCK RDMA dynamic library.
Features
- The primary and standby nodes share one copy of data, significantly reducing the storage capacity in traditional HA deployment mode.
- Log replication is not required between the primary and standby nodes. Instead, page exchange is implemented between the primary and standby nodes and real-time read consistency is supported on standby nodes.
- By default, the primary and standby nodes exchange pages in real time through the TCP network. To reduce the page exchange delay, the OCK RDMA dynamic library is introduced to improve the real-time consistency performance of the standby node.
Applicable Scenarios and Restrictions
- The storage device is a disk array. The LUN of the disk array must support the SCSI3 PR protocol, including PERSISTENT RESERVE OUT (PR OUT), PERSISTENT RESERVE IN (PR IN), and INQUIRY, to implement cluster IO FENCE. In addition, the COMPARE AND WRITE (CAW) protocol of SCSI3 must be supported to implement shared disk locks. For example, Dorado 5000 V3 disk array.
- A maximum of eight standby nodes can be deployed in openGauss.
- The primary/standby shared storage depends on functions similar to the distributed file system to implement the real-time read consistency on standby nodes. Therefore, the less the file metadata changes, the better. To ensure performance, this feature supports only segment-page tables.
- The primary and standby nodes must be deployed on the same disk array. DR deployment and hybrid deployment of the primary and standby nodes are not supported. For example, the primary and standby nodes are deployed on different disk arrays.
- Page exchange between the primary and standby nodes is accelerated by RDMA, depending on the CX5 NIC and OCK RDMA dynamic library.
- Currently, standby node rebuild, node replacement, and node restoration are not supported.
- Upgrade from the traditional HA deployment to the primary/standby shared storage deployment is not supported.
Manual Installation Example
Compared with traditional gs_initdb database creation, directories are classifies into three types during shared storage database creation: exclusively used and not shared by each instance, exclusively used and shared by each instance, and shared by all instances. The directories to be shared must be stored on the disk array, and the directories that are not shared must be stored on the local disk. In addition, to create a database on the standby node, you only need to create a directory that belongs to the standby node. You do not need to create a directory structure shared by all instances. GUC parameters are added to the primary/standby shared storage, and the storage mode of system catalogs is switched from page mode to segment-page mode.
NOTE: Step-by-step manual installation means that you can run related commands step by step to create a database for shared storage after project compilation. For details about how to install the openGauss, see the Installation Guide.
Prerequisites
- The code of the project has been compiled. For details about the compilation, see Software Compilation and Installation.
- The LUN of the disk array has been mounted to the host, the UltraPath software has been installed, and the disk array is available.
Procedure
Create symbolic links for drive letters of the disk array LUN and assign the corresponding permissions to the user. (Assume that the drive letters of the LUN are /dev/sde and /dev/sdf.)
sudo ln -s /dev/sde /dev/tpcc_data sudo ln -s /dev/sdf /dev/tpcc_log sudo chmod 777 /dev/tpcc_data sudo chmod 777 /dev/tpcc_logAssign the RAWIO permission of the disk array to the required executable files.
sudo -i setcap CAP_SYS_RAWIO+ep absolute path/perctrlperctrl: executable tool used to assign read and write permissions to DSS-related tools and processes.
Create a DSS server process and a configuration file required for creating a shared storage database.
Test directory (for example, /data/test)
└─dss_home/ ├── cfg │ ├── dss_inst.ini │ └── dss_vg_conf.ini └── log // The log directory must exist before the startup.The content of the dss_init.ini file is as follows:
INST_ID=0 _LOG_LEVEL=55 _LOG_BACKUP_FILE_COUNT=128 _LOG_MAX_FILE_SIZE =20M LSNR_PATH=/data/test/dss_home STORAGE_MODE=RAID _SHM_KEY=12The parameters in the preceding configuration are described as follows:
- INST_ID indicates the instance ID. The value ranges from 0 to 63. The value varies according to the primary and standby dssserver processes.
- _LOG_LEVEL indicates the log level.
- _LOG_BACKUP_FILE_COUNT indicates the maximum number of log files that can be retained.
- _LOG_MAX_FILE_SIZE indicates the maximum size of a log file.
- LSNR_PATH indicates the directory for storing the domain socket used for communication between the DSS client and server. Generally, it is set to the home directory of the DSS server process.
- STORAGE_MODE indicates the storage device type of the DSS. Set this parameter to RAID for disk arrays.
- _SHM_KEY indicates the shared memory key. Ensure that each DSS has a unique key.
The content of the dss_vg_conf.ini file is as follows:
data:/dev/tpcc_data log: /dev/tpcc_logThe preceding information indicates that the contents of the +data directory are stored on the /dev/tpcc_data device and the contents of the +log directory are stored on the /dev/tpcc_log device. Check whether the root directory name contains the plus sign (+) to determine whether a file is in the file system or DSS. DSS is regarded as a distributed file system.
Use the DSS client tool (dsscmd) to initialize the volume group (VG) on the disk array (similar to initializing the file system on a raw disk).
# Clear the beginning data of the disk array LUN. dd if=/dev/zero bs=2048 count=100000 of=/dev/tpcc_data dd if=/dev/zero bs=2048 count=100000 of=/dev/tpcc_log # Create a VG. dsscmd cv -g data -v /dev/tpcc_data -s 2048 -D /data/ss_test/dss_home dsscmd cv -g log -v /dev/tpcc_log -s 65536 -D /data/ss_test/dss_home # Start the dssserver. dssserver -D /data/ss_test/dss_home &Use gs_initdb to create a shared storage database.
gs_initdb -D /data/ss_test/dn_primary --nodename=single_node -w Gauss_234 --vgname="+data,+log" --enable-dss --dms_url="0:127.0.0.1:1611,1:127.0.0.1:1711" -I 0 --socketpath="UDS:/data/ss_test/dss_home/.dss_unix_d_socket"The following parameters are added:
- --vgname specifies the VG where the shared storage database is created. The VG name is related to the configuration item in the dss_vg_conf.ini file. The VG name must exist in the configuration file and start with a plus sign (+).
- --enable_dss indicates that the shared storage database created in DSS.
- --dms_url “0:127.0.0.1:1611,1:127.0.0.1:1711” indicates that format is Instance_ID**:IP address:**Port number.
- -I: specifies the instance ID of the current node. The value ranges from 0 to 63.
- --socketpath specifies the location of the Unix domain socket used for the communication between the DSS client (DSS client dynamic library integrated into the executable file of the database) and the server.
After the shared storage database is successfully created, run the gs_ctl start command to start the database process.
gs_ctl start -D /data/ss_test/dn_primaryRepeat the preceding installation procedure on the standby node.
OCK RDMA Usage Example
The shared storage feature provides the real-time read consistency function on standby nodes. RDMA can be used to accelerate page exchange between the primary and standby nodes. This section describes how to enable the RDMA communication function in the shared storage.
Prerequisites
The RDMA function depends on the CX5 NIC and OCK RPC dynamic library.
Procedure
Contact openGauss support to obtain OCK RPC package.
Deploy the OCK RPC package.
Decompress the OCK RPC package.
tar -zxf OCK_platform_rpc_22.0.0_EulerOS-aarch64.tar.gz cd OCK_platform_rpc_22.0.0_EulerOS-aarch64_release tar -zxf OCK_platform_rpc_EulerOS_aarch64.tar.gz tar -zxf OCK_platform_rpc_sbin.tar.gz cp rpc_sbin/ock_rpc_opengauss.sh ./Modify the parameters in the ock_rpc_opengauss.sh deployment script.
# Deployment user, which is the same as the opengauss user. # It is a non-root user. Ensure that this user exists on all servers. USER_NAME="${USER}" # Deployment server, which can contain native HOST_IP=(30.30.xx.7 30.30.xx.8) # Deployment package. The package name starts with OCK_platform_rpc. PACKAGES="OCK_platform_rpc_aarch64_EulerOS.tar.gz" # Specifies the path from the SCP package to the server. # If the path does not exist, the path is automatically created. PATH_TO_SCP="/home/ock/test" # Opengauss environment variable GAUSSHOME="/home/ock/mppdb_temp_install" # OCK_RPC environment variable. Do not change OCK_RPC_LIB_PATH="${GAUSSHOME}/lib"The parameters involved in the script are as follows:
- USER_NAME: user name of the host where the DN is located.
- HOST_IP: IP address of a cluster host, including the local host.
- PACKAGES: name of the obtained OCK RPC binary package (matching the host OS architecture).
- PATH_TO_SCP: copy path.
- GAUSSHOME: The value must be the same as the environment variable GAUSSHOME configured on openGauss.
- OCK_RPC_LIB_PATH: path of the OCK RPC binary file. The shared storage is used in dynamic loading mode. Ensure that the path is correct.
Run the deployment script ock_rpc_opengauss.sh.
sh ock_rpc_opengauss.sh NOTE:
Functions:
NOTE:
Functions:- The OCK RPC binary package in the cluster is deployed, decompressed, and copied.
- The environment variable $OCK_RPC_LIB_PATH is configured.
- The UCX environment variables are configured for cluster nodes. (UCX is a communication component developed based on RDMA, and OCK RPC is a communication component developed based on UCX to adapt to shared storage.)
Configure other environment variables.
export UCX_ZCOPY_THRESH="32768" export UCX_USE_MT_MUTEX=n export UCX_NET_DEVICES=mlx5_1:1Parameter description:
The UCX_ZCOPY_THRESH optimization parameter is used to reduce the memory application during RDMA transmission. Unit: byte. Default value: 32768. (This parameter is optional. The default value is recommended.)
The UCX_USE_MT_MUTEX optimization parameter is used to ensure the data consistency lock during RDMA transmission. The options are n (atomic lock) and y (mutex). (This parameter is optional. You are advised to use the atomic lock because the performance is good.)
The UCX_NET_DEVICES configuration parameter is used to specify the NIC port. You can install the mlnx_ofed driver and run the ibdev2netdev command to view the current active RDMA ports. (You are advised to specify active ports.)
 NOTE:
After the environment variables are configured, run the source ~/.bashrc command.
NOTE:
After the environment variables are configured, run the source ~/.bashrc command.
Modify the postgresql.conf file.
Set ss_interconnect_type to RDMA and add the ss_rdma_work_config and ss_ock_log_path configuration items. For details about the parameter description and configuration, see Shared Storage Parameters.
Example:
ss_interconnect_type=RDMA ss_rdma_work_config ='6 10' (Start and end CPUs used in the OCK RDMA user-mode poll, separated by a space.) ss_ock_log_path= "/home/ock_test/log" (Logs generated during OCK RDMA message communication)Run the gs_ctl start command to start the database process.
gs_ctl start -D /data/ss_test/dn_primary