ODBC
Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a Microsoft API for accessing databases based on the X/OPEN CLI. Applications interact with the database through the APIs provided by ODBC, which enhances their portability, scalability, and maintainability.
Figure 1 shows the system structure of ODBC.
Figure 1 ODBC system structure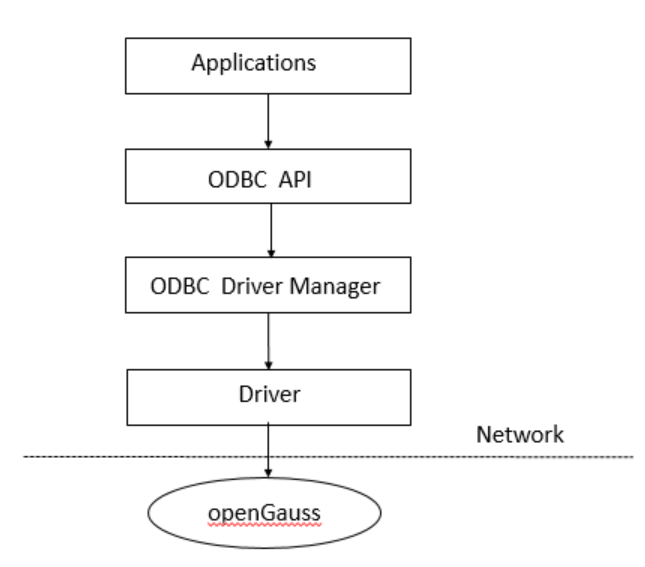
openGauss supports ODBC in the following environments.
Table 1 OSs Supported by ODBC
ODBC Packages for the Linux OS
Obtain the openGauss-*.*.0-ODBC.tar.gz package from the release package. In the Linux OS, unixODBC header files (including sql.h and sqlext.h) and a library file (libodbc.so) are required in application development. The header files and library file can be obtained from the unixODBC-2.3.0 installation package.
Configuring the Data Source
The ODBC driver (psqlodbcw.so) provided by openGauss can be used after it is configured in a data source. To configure a data source, you must configure the odbc.ini and odbcinst.ini files on the server. The two files are generated during the unixODBC compilation and installation, and are saved in the /usr/local/etc directory by default.
Obtain the unixODBC-2.3.9 source code package.
Download address: http://www.unixodbc.org/download.html
Install unixODBC. If the unixODBC of another version has been installed on the host, overwrite the existing unixODBC.
Currently, unixODBC-2.2.1 is not supported. For example, to install unixODBC-2.3.0, run the commands below. unixODBC is installed in the /usr/local directory by default. The data source file is generated in the /usr/local/etc directory, and the library file is generated in the /usr/local/lib directory.
tar zxvf unixODBC-2.3.9.tar.gz cd unixODBC-2.3.9 # Modify the configure file. (If it does not exist, modify the configure.ac file.) Find LIB_VERSION. # Change the value of LIB_VERSION to 1:0:0 to compile a *.so.1 dynamic library with the same dependency on psqlodbcw.so. vim configure ./configure --enable-gui=no # To perform compilation on an ARM server, add the **configure** parameter **--build=aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu**. make # The installation may require root permissions. make installReplace the openGauss client driver.
- Decompress openGauss-x.x.x-ODBC.tar.gz to the /usr/local/lib directory. The psqlodbcw.la and psqlodbcw.so files are obtained.
- Copy the library in the lib directory obtained after decompressing openGauss-x.x.x-ODBC.tar.gz to the /usr/local/lib directory.
Configure a data source.
Configure the ODBC driver file.
Add the following content to the /xxx/odbc/etc/odbcinst.ini file:
[GaussMPP] Driver64=/xxx/odbc/lib/psqlodbcw.so setup=/xxx/odbc/lib/psqlodbcw.soFor descriptions of the parameters in the odbcinst.ini file, see Table 2.
Table 2 odbcinst.ini configuration parameters
Driver installation path, which is the same as the dynamic library path in Driver64.
Configure the data source file.
Add the following content to the /usr/local/etc/odbc.ini file:
[MPPODBC] Driver=GaussMPP Servername=10.145.130.26 (IP address of the server where the database resides) Database=postgres (Database name) Username=omm (Database username) Password= (User password of the database) Port=8000 (Listening port of the database) Sslmode=allowFor descriptions of the parameters in the odbc.ini file, see Table 3.
Table 3 odbc.ini configuration parameters
The valid values of Sslmode are as follows:
Table 4 Sslmode options
 NOTE:
SSL mode:
Ensure that the permission on the client.key* series files is 600.
Go back to the root directory, create the .postgresql directory, and save root.crt, client.crt, client.key, client.key.cipher, client.key.rand, client.req, server.crt, server.key, server.key.cipher, server.key.rand, and server.req to the .postgresql directory.
In the Unix OS, server.crt and server.key must deny the access from the external system or any group. Run the following command to set this permission:
NOTE:
SSL mode:
Ensure that the permission on the client.key* series files is 600.
Go back to the root directory, create the .postgresql directory, and save root.crt, client.crt, client.key, client.key.cipher, client.key.rand, client.req, server.crt, server.key, server.key.cipher, server.key.rand, and server.req to the .postgresql directory.
In the Unix OS, server.crt and server.key must deny the access from the external system or any group. Run the following command to set this permission:chmod 0600 server.keyCopy the certificate files whose names start with root.crt and server to the install/data directory of the database (the directory is the same as that of the postgresql.conf file). Modify the postgresql.conf file.
ssl = on ssl_cert_file = 'server.crt' ssl_key_file = 'server.key' ssl_ca_file = 'root.crt'After modifying the parameters, restart the database. Set the sslmode parameter to require or verify-ca in the odbc.ini file.
Configure the database server.
Log in as the OS user omm to the primary database node.
Run the following command to add NIC IP addresses or host names which are separated by commas (,). The NICs and hosts are used to provide external services. In the following command, NodeName specifies the name of the current node.
gs_guc reload -N NodeName -I all -c "listen_addresses='localhost,192.168.0.100,10.11.12.13'"If direct routing of LVS is used, add the virtual IP address (10.11.12.13) of LVS to the server listening list.
You can also set listen_addresses to * or 0.0.0.0 to listen on all NICs, but this incurs security risks and is not recommended.
Run the following command to add an authentication rule to the configuration file of the primary database node. In this example, the IP address (10.11.12.13) of the client is the remote host IP address.
gs_guc reload -N all -I all -h "host all jack 10.11.12.13/32 sha256" NOTE:
NOTE:- -N all indicates all hosts in openGauss.
- -I all indicates all instances of the host.
- -h specifies statements that need to be added in the pg_hba.conf file.
- all indicates that a client can connect to any database.
- jack indicates the user that accesses the database.
- 10.11.12.13/__32 indicates hosts whose IP address is 10.11.12.13 can be connected. Configure the parameter based on your network conditions. 32 indicates that there are 32 bits whose value is 1 in the subnet mask. That is, the subnet mask is 255.255.255.255.
- sha256 indicates that the password of user jack is encrypted using the SHA-256 algorithm.
If the ODBC client and the primary database node to connect are deployed on the same machine, you can use the local trust authentication mode. Run the following command:
local all all trustIf the ODBC client and the primary database node to connect are deployed on different machines, use the SHA-256 authentication mode. Run the following command:
host all all xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/32 sha256Restart openGauss.
gs_om -t stop gs_om -t start
Configure the environment variables on the client.
vim ~/.bashrcAdd the following information to the configuration file:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/lib/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH export ODBCSYSINI=/usr/local/etc export ODBCINI=/usr/local/etc/odbc.iniRun the following command to validate the addition:
source ~/.bashrc
Verifying the Data Source Configuration
Run the ./isql -v MPPODBC command (MPPODBC is the data source name).
If the following information is displayed, the configuration is correct and the connection succeeds.
+---------------------------------------+ | Connected! | | | | sql-statement | | help [tablename] | | quit | | | +---------------------------------------+ SQL>If error information is displayed, the configuration is incorrect. Check the configuration.
Development Process
Figure 2 ODBC-based application development process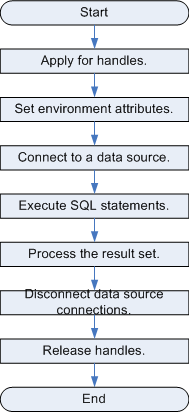
Common APIs
Table 5 API description
SQLAllocHandle is a generic function for allocating handles. It can replace the following functions:
| |
SQLFreeHandle is a generic function for releasing a handle. It can replace the following functions:
|
NOTE: If an execution request (not in a transaction block) received in the database contains multiple statements, the request is packed into a transaction. If one of the statements fails, the entire request will be rolled back.
Connecting to a Database
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sqlext.h>
#ifdef WIN32
#include <windows.h>
#endif
SQLHENV V_OD_Env; // Handle ODBC environment
SQLHDBC V_OD_hdbc; // Handle connection
SQLINTEGER V_OD_erg;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
// 1. Allocate an environment handle.
V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV,SQL_NULL_HANDLE,&V_OD_Env);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
printf("Error AllocHandle\n");
exit(0);
}
// 2. Set environment attributes (version information).
SQLSetEnvAttr(V_OD_Env, SQL_ATTR_ODBC_VERSION, (void*)SQL_OV_ODBC3, 0);
// 3. Allocate a connection handle.
V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC, V_OD_Env, &V_OD_hdbc);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
exit(0);
}
// 4. Set connection attributes.
SQLSetConnectAttr(V_OD_hdbc, SQL_ATTR_AUTOCOMMIT, SQL_AUTOCOMMIT_ON, 0);
// 5. Connect to a data source. userName and password indicate the username and password for connecting to the database. Set them as needed.
// If the username and password have been set in the odbc.ini file, you do not need to set userName or password here, retaining "" for them. However, you are not advised to do so because the username and password will be disclosed if the permission for odbc.ini is abused.
V_OD_erg = SQLConnect(V_OD_hdbc, (SQLCHAR*) "gaussdb", SQL_NTS,
(SQLCHAR*) "userName", SQL_NTS, (SQLCHAR*) "password", SQL_NTS);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
printf("Error SQLConnect %d\n",V_OD_erg);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
exit(0);
}
printf("Connected !\n");
// 6. Disconnect data source connections and release handles.
SQLDisconnect(V_OD_hdbc);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC,V_OD_hdbc);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
return(0);
}
Creating a Table
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sqlext.h>
#ifdef WIN32
#include <windows.h>
#endif
SQLHENV V_OD_Env; // Handle ODBC environment
SQLHSTMT V_OD_hstmt; // Handle statement
SQLHDBC V_OD_hdbc; // Handle connection
SQLINTEGER V_OD_erg;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV,SQL_NULL_HANDLE,&V_OD_Env);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
printf("Error AllocHandle\n");
exit(0);
}
SQLSetEnvAttr(V_OD_Env, SQL_ATTR_ODBC_VERSION, (void*)SQL_OV_ODBC3, 0);
V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC, V_OD_Env, &V_OD_hdbc);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
exit(0);
}
SQLSetConnectAttr(V_OD_hdbc, SQL_ATTR_AUTOCOMMIT, SQL_AUTOCOMMIT_ON, 0);
V_OD_erg = SQLConnect(V_OD_hdbc, (SQLCHAR*) "gaussdb", SQL_NTS,
(SQLCHAR*) "userName", SQL_NTS, (SQLCHAR*) "password", SQL_NTS);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
printf("Error SQLConnect %d\n",V_OD_erg);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
exit(0);
}
printf("Connected !\n");
// 1. Set statement attributes.
SQLSetStmtAttr(V_OD_hstmt,SQL_ATTR_QUERY_TIMEOUT,(SQLPOINTER *)3,0);
// 2. Apply for statement handles.
SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT, V_OD_hdbc, &V_OD_hstmt);
// 3. Create a table.
SQLExecDirect(V_OD_hstmt,"drop table IF EXISTS customer_t1",SQL_NTS);
SQLExecDirect(V_OD_hstmt,"CREATE TABLE customer_t1(c_customer_sk INTEGER, c_customer_name VARCHAR(32));",SQL_NTS);
printf("Done !\n");
// 4. Disconnect data source connections and release handles.
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT,V_OD_hstmt);
SQLDisconnect(V_OD_hdbc);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC,V_OD_hdbc);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
return(0);
}
Insert Operation
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sqlext.h>
#ifdef WIN32
#include <windows.h>
#endif
SQLHENV V_OD_Env; // Handle ODBC environment
SQLHSTMT V_OD_hstmt; // Handle statement
SQLHDBC V_OD_hdbc; // Handle connection
SQLINTEGER value = 100;
SQLINTEGER V_OD_erg;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV,SQL_NULL_HANDLE,&V_OD_Env);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
printf("Error AllocHandle\n");
exit(0);
}
SQLSetEnvAttr(V_OD_Env, SQL_ATTR_ODBC_VERSION, (void*)SQL_OV_ODBC3, 0);
V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC, V_OD_Env, &V_OD_hdbc);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
exit(0);
}
SQLSetConnectAttr(V_OD_hdbc, SQL_ATTR_AUTOCOMMIT, SQL_AUTOCOMMIT_ON, 0);
V_OD_erg = SQLConnect(V_OD_hdbc, (SQLCHAR*) "gaussdb", SQL_NTS,
(SQLCHAR*) "userName", SQL_NTS, (SQLCHAR*) "password", SQL_NTS);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
printf("Error SQLConnect %d\n",V_OD_erg);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
exit(0);
}
printf("Connected !\n");
SQLSetStmtAttr(V_OD_hstmt,SQL_ATTR_QUERY_TIMEOUT,(SQLPOINTER *)3,0);
SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT, V_OD_hdbc, &V_OD_hstmt);
// 1. Insert directly.
SQLExecDirect(V_OD_hstmt,"insert into customer_t1 values(25,li)",SQL_NTS);
// 2. Insert the pbe method.
// 2.1 Insert a placeholder.
SQLPrepare(V_OD_hstmt,"insert into customer_t1 values(?)",SQL_NTS);
// 2.2 Bind parameters.
SQLBindParameter(V_OD_hstmt,1,SQL_PARAM_INPUT,SQL_C_SLONG,SQL_INTEGER,0,0,
&value,0,NULL);
// 2.3 Execute the prepared insert statement.
SQLExecute(V_OD_hstmt);
// 3. Disconnect data source connections and release handles.
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT,V_OD_hstmt);
SQLDisconnect(V_OD_hdbc);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC,V_OD_hdbc);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
return(0);
}
SELECT Operation
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sqlext.h>
#ifdef WIN32
#include <windows.h>
#endif
SQLHENV V_OD_Env; // Handle ODBC environment
SQLHSTMT V_OD_hstmt; // Handle statement
SQLHDBC V_OD_hdbc; // Handle connection
char typename[100];
SQLINTEGER V_OD_erg, V_OD_buffer, V_OD_err, V_OD_id;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV,SQL_NULL_HANDLE,&V_OD_Env);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
printf("Error AllocHandle\n");
exit(0);
}
SQLSetEnvAttr(V_OD_Env, SQL_ATTR_ODBC_VERSION, (void*)SQL_OV_ODBC3, 0);
V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC, V_OD_Env, &V_OD_hdbc);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
exit(0);
}
SQLSetConnectAttr(V_OD_hdbc, SQL_ATTR_AUTOCOMMIT, SQL_AUTOCOMMIT_ON, 0);
V_OD_erg = SQLConnect(V_OD_hdbc, (SQLCHAR*) "gaussdb", SQL_NTS,
(SQLCHAR*) "userName", SQL_NTS, (SQLCHAR*) "password", SQL_NTS);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
printf("Error SQLConnect %d\n",V_OD_erg);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
exit(0);
}
printf("Connected !\n");
SQLSetStmtAttr(V_OD_hstmt,SQL_ATTR_QUERY_TIMEOUT,(SQLPOINTER *)3,0);
SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT, V_OD_hdbc, &V_OD_hstmt);
// 1. Run the select statement.
SQLExecDirect(V_OD_hstmt,"select c_customer_sk from customer_t1",SQL_NTS);
// 2. Obtain attributes of a specific column in the result set.
SQLColAttribute(V_OD_hstmt,1,SQL_DESC_TYPE,typename,100,NULL,NULL);
printf("SQLColAtrribute %s\n",typename);
// 3. Bind the result set.
SQLBindCol(V_OD_hstmt,1,SQL_C_SLONG, (SQLPOINTER)&V_OD_buffer,150,
(SQLLEN *)&V_OD_err);
// 4. Obtain data in the result set by executing SQLFetch.
V_OD_erg=SQLFetch(V_OD_hstmt);
// 5. Obtain and return data by executing SQLGetData.
while(V_OD_erg != SQL_NO_DATA)
{
SQLGetData(V_OD_hstmt,1,SQL_C_SLONG,(SQLPOINTER)&V_OD_id,0,NULL);
printf("SQLGetData ----ID = %d\n",V_OD_id);
V_OD_erg=SQLFetch(V_OD_hstmt);
};
printf("Done !\n");
// 6. Disconnect data source connections and release handles.
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT,V_OD_hstmt);
SQLDisconnect(V_OD_hdbc);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC,V_OD_hdbc);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
return(0);
}
Update Operation
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sqlext.h>
#ifdef WIN32
#include <windows.h>
#endif
SQLHENV V_OD_Env; // Handle ODBC environment
SQLHSTMT V_OD_hstmt; // Handle statement
SQLHDBC V_OD_hdbc; // Handle connection
SQLINTEGER V_OD_erg;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV,SQL_NULL_HANDLE,&V_OD_Env);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
printf("Error AllocHandle\n");
exit(0);
}
SQLSetEnvAttr(V_OD_Env, SQL_ATTR_ODBC_VERSION, (void*)SQL_OV_ODBC3, 0);
V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC, V_OD_Env, &V_OD_hdbc);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
exit(0);
}
SQLSetConnectAttr(V_OD_hdbc, SQL_ATTR_AUTOCOMMIT, SQL_AUTOCOMMIT_ON, 0);
V_OD_erg = SQLConnect(V_OD_hdbc, (SQLCHAR*) "gaussdb", SQL_NTS,
(SQLCHAR*) "userName", SQL_NTS, (SQLCHAR*) "password", SQL_NTS);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
printf("Error SQLConnect %d\n",V_OD_erg);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
exit(0);
}
printf("Connected !\n");
SQLSetStmtAttr(V_OD_hstmt,SQL_ATTR_QUERY_TIMEOUT,(SQLPOINTER *)3,0);
SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT, V_OD_hdbc, &V_OD_hstmt);
// 1. Perform the update operation.
SQLExecDirect(V_OD_hstmt,"update customer_t1 set c_customer_sk = 1000 where c_customer_name = 'li' ",SQL_NTS);
// 16. Disconnect data source connections and release handles.
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT,V_OD_hstmt);
SQLDisconnect(V_OD_hdbc);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC,V_OD_hdbc);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
return(0);
}
Delete Operation
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sqlext.h>
#ifdef WIN32
#include <windows.h>
#endif
SQLHENV V_OD_Env; // Handle ODBC environment
SQLHSTMT V_OD_hstmt; // Handle statement
SQLHDBC V_OD_hdbc; // Handle connection
SQLINTEGER V_OD_erg;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV,SQL_NULL_HANDLE,&V_OD_Env);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
printf("Error AllocHandle\n");
exit(0);
}
SQLSetEnvAttr(V_OD_Env, SQL_ATTR_ODBC_VERSION, (void*)SQL_OV_ODBC3, 0);
V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC, V_OD_Env, &V_OD_hdbc);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
exit(0);
}
SQLSetConnectAttr(V_OD_hdbc, SQL_ATTR_AUTOCOMMIT, SQL_AUTOCOMMIT_ON, 0);
V_OD_erg = SQLConnect(V_OD_hdbc, (SQLCHAR*) "gaussdb", SQL_NTS,
(SQLCHAR*) "userName", SQL_NTS, (SQLCHAR*) "password", SQL_NTS);
if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO))
{
printf("Error SQLConnect %d\n",V_OD_erg);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
exit(0);
}
printf("Connected !\n");
SQLSetStmtAttr(V_OD_hstmt,SQL_ATTR_QUERY_TIMEOUT,(SQLPOINTER *)3,0);
SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT, V_OD_hdbc, &V_OD_hstmt);
// 1. Perform the delete operation.
SQLExecDirect(V_OD_hstmt,"delete from customer_t1 where c_customer_name = 'li'",SQL_NTS);
// 2. Disconnect data source connections and release handles.
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT,V_OD_hstmt);
SQLDisconnect(V_OD_hdbc);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC,V_OD_hdbc);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env);
return(0);
}