SMP Application Scenarios and Restrictions
Context
The SMP feature improves the performance through operator parallelism and occupies more system resources, including CPU, memory, and I/O. Actually, SMP is a method consuming resources to save time. It improves system performance in appropriate scenarios and when resources are sufficient, but may deteriorate performance otherwise. SMP applies to analytical query scenarios where a single query takes a long time and the service concurrency is low. The SMP parallel technology can reduce the query delay and improve the system throughput performance. However, in a high transactional concurrency scenario, a single query has a short delay. In this case, using a multi-thread parallel technology increases the query delay and reduces the system throughput performance.
Application Scenarios
Operators that support parallelism. The plan contains the following operators that support parallelism.
- Scan: Row-store ordinary tables and row-store partitioned tables, and column-store ordinary tables and column-store partitioned tables can be sequentially scanned.
- Join: HashJoin and NestLoop
- Agg: HashAgg, SortAgg, PlainAgg, and WindowAgg (which supports only partition by, and does not support order by)
- Stream: Local Redistribute and Local Broadcast
- Others: Result, Subqueryscan, Unique, Material, Setop, Append, VectoRow, and RowToVec
SMP-specific operators: To execute queries in parallel, Stream operators are added for data exchange of the SMP feature. These new operators can be considered as the subtypes of Stream operators.
- Local Gather aggregates data of parallel threads within an instance.
- Local Redistribute redistributes data based on the distributed key across threads within an instance.
- Local Broadcast broadcasts data to each thread within an instance.
- Local RoundRobin distributes data in polling mode across threads within an instance.
The following uses the TPCH Q1 parallel plan as an example.
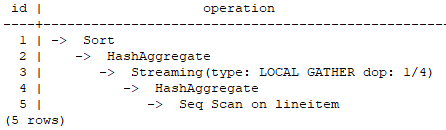
In this plan, the Scan and HashAgg operators are processed in parallel, and the Local Gather operator is added for data exchange. Operator 3 is a Local Gather operator. “dop: 1/4” indicates that the degree of parallelism of the sender thread is 4 and the degree of parallelism of the receiver thread is 1. That is, the lower-layer HashAggregate operator 4 is executed based on the degree of parallelism 4, the upper-layer operators 1 and 2 are executed in serial mode, and operator 3 aggregates data of parallel threads within the instance.
You can view the parallelism situation of each operator in the dop information.
Non-applicable Scenarios
- Index scanning cannot be executed in parallel.
- MergeJoin cannot be executed in parallel.
- WindowAgg order by cannot be executed in parallel.
- The cursor cannot be executed in parallel.
- Queries in stored procedures and functions cannot be executed in parallel.
- Subplans and initplans cannot be queried in parallel, and operators that contain subqueries cannot be executed in parallel, either.
- Query statements that contain the median operation cannot be executed in parallel.
- Queries with global temporary tables cannot be executed in parallel.
- Updating materialized views cannot be executed in parallel.